Tasuki gap patterns are fairly rare but give a clear signal.
Since candlesticks are the basic building block of most technical analysis, the ability to recognize different candlestick patterns is a crucial trading skill.
In this Guide to Tasuki Gap Patterns, we’ll explain:
First though, let’s start with a definition.
What Is a Tasuki Gap Pattern?
A tasuki gap pattern is a 3-candlestick formation that may signal a continuation. It is made up of a candle moving in the direction of trend, followed by a gap, another candle moving in the direction of trend, and then a candle moving against trend that partially closes the gap between the first two.
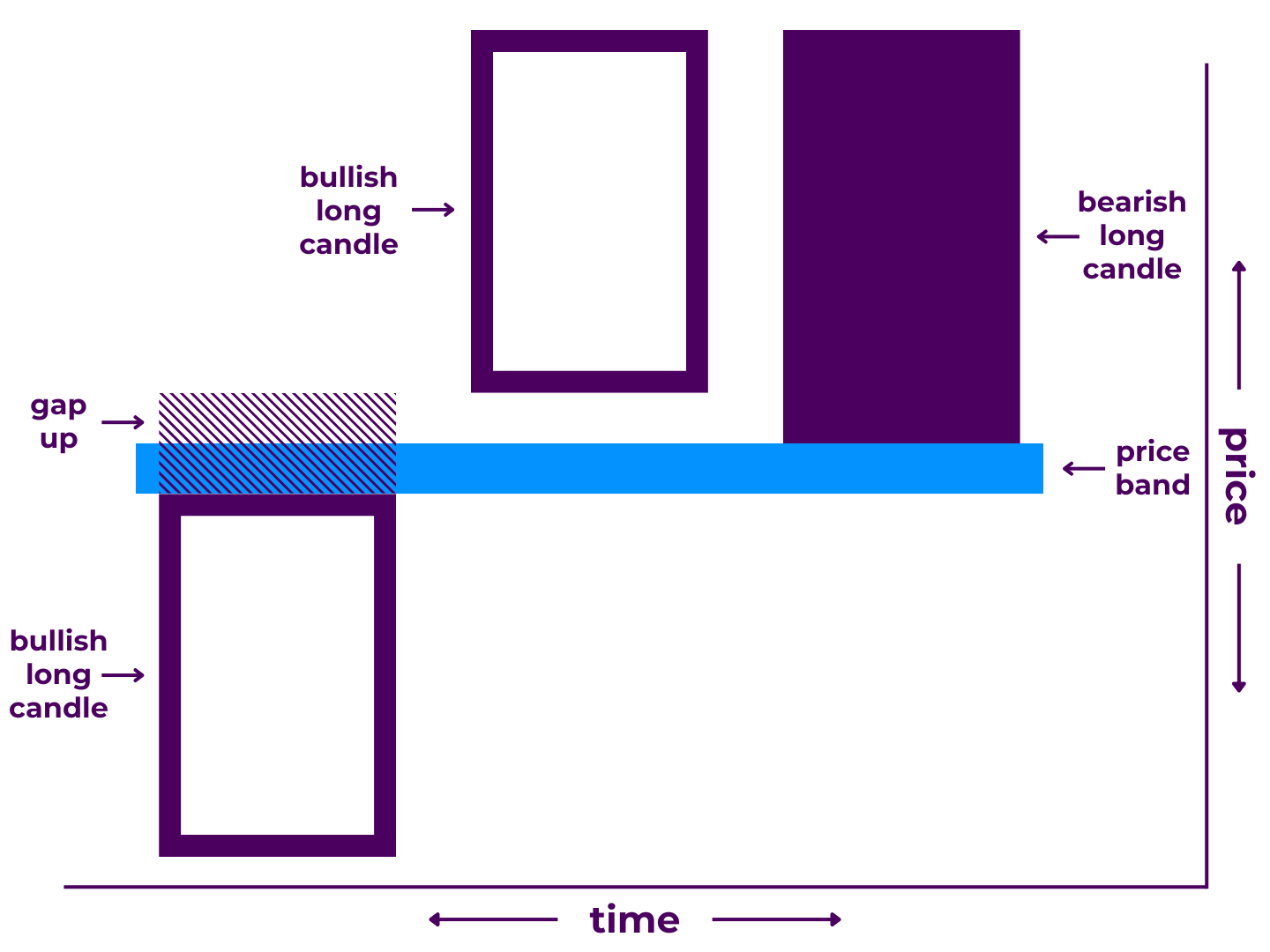
The tasuki gap has both bullish and bearish variations, called the upside tasuki gap and downside tasuki gap, respectively. It is essentially an extension of the window pattern. For both, the unfilled gap represents a make-or-break price band that could shape upcoming price action.
Of course, no candlestick pattern guarantees a particular outcome. Instead, they offer clues as to what is going on in the market.
So the question is, what does a tasuki gap really tell you?
What Tasuki Gap Patterns Mean
Like many candlestick patterns, the name itself doesn’t reveal much.
In Japanese, a tasuki is a type of sash used to hold up the sleeves of a kimono. We have no idea how the two relate but are 99% sure they do in some way.
(If you know the true meaning, please leave it in the comments below).
In trading terms:
- During the first period, price drove strongly in the direction of trend.
- Between periods, price continued driving in the same direction.
- During the second period, price yet again continued driving in the direction of trend.
- During the third period, price moved against trend to close somewhere in the middle of the gap.
This sets the stage for continuation, as countertrend pressure failed to close the gap.
How To Recognize Tasuki Gap Candlestick Patterns
Traders are attracted to patterns partly because they are easy to spot.
However, it’s also easy to see things on the charts that aren’t truly there (or anticipate events that never come to fruition). That’s one of the reasons why waiting for confirmation is so important.
Technically, a tasuki gap pattern must:
- Begin with a long candle moving with trend
- Have a trend-side gap after the first candle
- Have a second long candle moving with trend after the gap
- End with a long candle moving against trend that partially fills the gap
In practicality though, many traders will make various exceptions.
- The first candle doesn’t necessarily have to be a long candle, as long as it is a candlestick that gives a strong bias in the direction of trend (such as a dragonfly doji or gravestone doji).
- The second candle doesn’t necessarily have to be a long candle, as long as the first one is and the gap remains unfilled.
- The third candle doesn’t necessarily have to be a long candle, as long as it doesn’t fully fill the gap and moves against trend.
- The third candle doesn’t have to fill the gap at all, as long as it moves against trend.
- It can take multiple countertrend candles to reach the gap, as long as all other criteria are met and the gap remains partially unfilled.
Depending on who you ask, any of these standards may be more or less important. Moreover, some of these variations may be more properly classified as other continuation candlestick patterns, such as the window.
Remember, identifying the continuation itself is more important than labeling the formation. That’s not to say these standards are completely unimportant (as we’ll touch on shortly). It’s just to say that the implications are more important than the criteria.
In other words, you need to put it into context.
Where Tasuki Gaps Fit in the Chart Narrative
The markets are often characterized as a battle between the bulls and the bears.
Tasuki gap patterns show that one side pressed their advantage on candle one, continued between candles one and two, continued further through the end of two, until finally suffering a relatively minor setback on candle three.
On the chart, it looks like a momentary respite.
It might happen like this on a daily time frame:
After a strongly trending day, traders awoke the next day to price gap. Fearful, those on the opposite side of trend back off. This lack of pushback leads to another large move in the direction of trend. Happy with their gains, trend-side traders take profits on the third day, giving the opposition an opportunity to fill the gap. They get close, but are unable to fill the gap completely by the end of the third day.
In the short-term, it amounts to an attempted counterattack.
The question traders need to ask themselves is, “Will the gap stand up as a base for continuation or can countertrend pressure rally to close it and stem the tide?”
To answer that question, you’ll need more than just an understanding of Japanese candlesticks and candlestick patterns. You’ll want to analyze both within the context of greater chart patterns as well as trend and price levels. You’ll also want to make use of your own chart markup and indicators.
Analyze the history of your preferred asset(s) with respect to tasuki gap patterns and apply it to your own trading style.
Now, you can test (and/or stretch) the criteria we mentioned above to find the most tradeable opportunities. For example, you may find that tasuki gaps with larger gaps play out more reliably than those with smaller gaps. Or, you may find something else entirely.
Here is where the story in the charts begins to come into focus.
This is what we call technical analysis.
How To Trade Tasuki Gap Patterns
Continuation patterns are great places to add to your position or adjust your stop loss.
Tasuki gap patterns serve as easy-to-spot signs of potential continuation that may serve as a staging ground for the next big leg up or leg down.
Generally, you can put more weight into multi-stick patterns than single candles. They give you more information over a longer amount of time. Still, it is considered unwise to trade based on candlestick patterns alone. They rarely have extremely high hit rates by themselves.
You need additional points of confluence to shift the probabilities in your favor.
Some of the more important ones include:
- Volume – Conventional wisdom says that the likelihood of continuation increases with higher trading volume on the first and second candles and lower volume on the third.
- Price Formations – Continuation patterns like the tasuki gap tend to perform better when there is thin support or resistance in their way. If it’s a blue sky breakout, even better.
- Matching Momentum – Oscillating indicators like the RSI or stochastics are commonly used to identify continuation by analyzing slope, percentile, and/or divergence.
The fewer such factors corroborating the continuation, the less confident you can be about it.
It would be difficult to form a comprehensive trading strategy around tasuki gap patterns. There simply isn’t enough there to develop a strong edge. Even with a great understanding of trading math, orders, psychology, risk management, options, and automation, you’d still have a hard time.
You’re much better off building your strategy around other tools then using continuation patterns as an additional point of confirmation.
Patterns like the tasuki gap are much better idea givers than trade makers.
Other Candlestick Pattern Types
The tasuki gap is but one of many candlestick patterns.
You’d be wise to get familiar with all of the other ones too.
- Abandoned Baby
- Breakaway
- Counterattack Lines
- Doji Star
- Engulfing
- Gap Three Methods
- Harami
- Harami Cross
- In Neck
- Kicking
- Ladder
- Last Engulfing
- Mat Hold
- Matching
- Meeting Lines
- On Neck
- Separating Lines
- Star
- Stomach
- Three Inside
- Three Methods
- Three Outside
- Three-Line Strike
- Tri-Star
- Tweezer
- Window
Sure, there are quite a few of them. But don’t let that intimidate you.
It’s unnecessary to memorize all the names and criteria for every pattern. What’s more important is to learn the principles of price action and technical analysis.
In fact, you’re free to forget all of the names and specifications as long as you can look at a group of candlesticks and understand what they are trying to tell you.
Takeaways
To review:
Tasuki gaps are a type of candlestick pattern that signals a potential continuation. While not a guarantee, their appearance may indicate that market conditions are going to remain the same. Thus, they can help you find winning trades.
Of course, there are other candlestick patterns that you should learn about. And even so, the ability to recognize patterns is not enough to trade successfully on its own.
Nonetheless, you’ve now added one more tool to your toolkit.
Have questions or more information to add? Contribute to the conversation in the comments below! Or, if you know someone who could benefit from this post, share it with them. You can also check out our Candlestick Patterns Guide to improve your candlestick analysis skills.

0 Comments